Characterization of a Bioengineered AAV3B Capsid Variant with Enhanced Hepatocyte Tropism and Immune Evasion
- PMID: 36950804
- PMCID: PMC10125406
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2022.176
Characterization of a Bioengineered AAV3B Capsid Variant with Enhanced Hepatocyte Tropism and Immune Evasion
Abstract
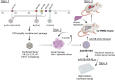
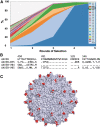
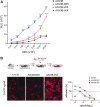
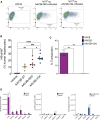
Capsid engineering of adeno-associated virus (AAV) can surmount current limitations to gene therapy such as broad tissue tropism, low transduction efficiency, or pre-existing neutralizing antibodies (NAb) that restrict patient eligibility. We previously generated an AAV3B combinatorial capsid library by integrating rational design and directed evolution with the aim of improving hepatotropism. A potential isolate, AAV3B-DE5, gained a selective proliferative advantage over five rounds of iterative selection in hepatocyte spheroid cultures. In this study, we reanalyzed our original dataset derived from the AAV3B combinatorial library and isolated variants from earlier (one to three) rounds of selection, with the assumption that variants with faster replication kinetics are not necessarily the most efficient transducers. We identified a potential candidate, AAV3B-V04, which demonstrated significantly enhanced transduction in mouse-passaged primary human hepatocytes as well as in humanized liver chimeric mice, compared to the parental AAV3B or the previously described isolate, AAV3B-DE5. Interestingly, the AAV3B-V04 capsid variant exhibited significantly reduced seroreactivity to pooled or individual human serum samples. Forty-four percent of serum samples with pre-existing NAbs to AAV3B had 5- to 20-fold lower reciprocal NAb titers to AAV3B-V04. AAV3B-V04 has only nine amino acid substitutions, clustered in variable region IV compared to AAV3B, indicating the importance of the loops at the top of the three-fold protrusions in determining both transduction efficiency and immunogenicity. This study highlights the effectiveness of rational design combined with targeted selection for enhanced AAV transduction via molecular evolution approaches. Our findings support the concept of limiting selection rounds to isolate the best transducing AAV3B variant without outgrowth of faster replicating candidates. We conclude that AAV3B-V04 provides advantages such as improved human hepatocyte tropism and immune evasion and propose its utility as a superior candidate for liver gene therapy.
Keywords: AAV3B; directed evolution; gene therapy; hepatocyte; huFNRG mice; humanized liver chimeric mice; neutralizing antibody; seroprevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Engineering and In Vitro Selection of a Novel AAV3B Variant with High Hepatocyte Tropism and Reduced Seroreactivity.Biswas M, Marsic D, Li N, Zou C, Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza G, Zolotukhin I, Kumar SRP, Rana J, Butterfield JSS, Kondratov O, de Jong YP, Herzog RW, Zolotukhin S. Biswas M, et al. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020 Oct 4;19:347-361. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.09.019. eCollection 2020 Dec 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020. PMID: 33145371 Free PMC article.
-
Coevolution of Adeno-associated Virus Capsid Antigenicity and Tropism through a Structure-Guided Approach.Havlik LP, Simon KE, Smith JK, Klinc KA, Tse LV, Oh DK, Fanous MM, Meganck RM, Mietzsch M, Kleinschmidt J, Agbandje-McKenna M, Asokan A. Havlik LP, et al. J Virol. 2020 Sep 15;94(19):e00976-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00976-20. Print 2020 Sep 15. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32669336 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered adeno-associated virus 3 vector with reduced reactivity to serum antibodies.Ito M, Takino N, Nomura T, Kan A, Muramatsu SI. Ito M, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 29;11(1):9322. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88614-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33927271 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of AAV vectors to target persistent viral reservoirs.Colón-Thillet R, Jerome KR, Stone D. Colón-Thillet R, et al. Virol J. 2021 Apr 23;18(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01555-7. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 33892762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Adeno-Associated Virus Serotypes and Engineered Adeno-Associated Virus Capsid Variants: Tropism Differences and Mechanistic Insights.Lopez-Gordo E, Chamberlain K, Riyad JM, Kohlbrenner E, Weber T. Lopez-Gordo E, et al. Viruses. 2024 Mar 12;16(3):442. doi: 10.3390/v16030442. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene therapy for hemophilia - From basic science to first approvals of "one-and-done" therapies.Herzog RW, Kaczmarek R, High KA. Herzog RW, et al. Mol Ther. 2025 May 7;33(5):2015-2034. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.03.043. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40156189 Review.
-
Revolution of AAV in Drug Discovery: From Delivery System to Clinical Application.Yin L, He H, Zhang H, Shang Y, Fu C, Wu S, Jin T. Yin L, et al. J Med Virol. 2025 Jun;97(6):e70447. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70447. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 40536197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mice Engrafted with Human Liver Cells.de Jong YP. de Jong YP. Semin Liver Dis. 2024 Nov;44(4):405-415. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1790601. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Semin Liver Dis. 2024. PMID: 39265638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B cell focused transient immune suppression protocol for efficient AAV readministration to the liver.Rana J, Herzog RW, Muñoz-Melero M, Yamada K, Kumar SRP, Lam AK, Markusic DM, Duan D, Terhorst C, Byrne BJ, Corti M, Biswas M. Rana J, et al. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Feb 20;32(1):101216. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101216. eCollection 2024 Mar 14. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 38440160 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Design of AAV-rh74, AAV3B, and AAV8 with Limited Liver Targeting.Chan C, Harris KK, Zolotukhin S, Keeler GD. Chan C, et al. Viruses. 2023 Oct 28;15(11):2168. doi: 10.3390/v15112168. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38005848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nathwani AC, Gray JT, Ng CY, et al. . Self-complementary adeno-associated virus vectors containing a novel liver-specific human factor IX expression cassette enable highly efficient transduction of murine and nonhuman primate liver. Blood 2006;107(7):2653–61; doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-10-4035 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mingozzi F, Liu YL, Dobrzynski E, et al. . Induction of immune tolerance to coagulation factor IX antigen by in vivo hepatic gene transfer. J Clin Invest 2003;111(9):1347–56; doi: 10.1172/JCI16887 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colella P, Ronzitti G, Mingozzi F. Emerging issues in AAV-mediated in vivo gene therapy. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 2018;8:87–104; doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2017.11.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maestro S, Weber ND, Zabaleta N, et al. . Novel vectors and approaches for gene therapy in liver diseases. JHEP Rep 2021;3(4):100300; doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100300 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grieger JC, Samulski RJ. Packaging capacity of adeno-associated virus serotypes: Impact of larger genomes on infectivity and postentry steps. J Virol 2005;79(15):9933–9944; doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9933-9944.2005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
MeSH terms
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
Substances
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
- Actions
- Search in PubMed
- Search in MeSH
- Add to Search
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
- Atypon
- Europe PubMed Central
- PubMed Central

